paginate
Allows to paginate an array of objects. Inside the paginate tag a paginate object will be available.
Accepts the following arguments:
object_array
an Array of objects, for example site.pages. (Required)
per_page
amount of items shown per page. (Not required, default: 10)
window_size
how many pages should be visible from the current page. E.g. if the current page is 5, and window size is 2, the pages available will be 3, 4, 5, 6, 7. Note that the first and the last page are always visible. (Not required, default: 3)
pagination_name
The name of the url parameter that is used to determine the current pagination number. This allows to paginate multiple arrays of objects. (Not required, default: “page”)
{% paginate ... pagination_name: "turn" %}/the-paginated-content?turn=4 # 4th pagination pageThe following code will paginate all projects of the site. On each page, 2 projects will be available.
{% paginate object_array: site.projects, per_page: 2, window_size: 2 %}
<h1>Current page: {{paginate.current_page}}</h1>
{% for project in paginate.items %}
<h3>{{project.title}}</h3>
{% endfor %}
<a href="{{paginate.previous.url}}">« Prev</a>
<ul>
{% for pagination_page in paginate.pages %}
<li><a href="{{pagination_page.url}}">{{pagination_page.index}}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<a href="{{paginate.next.url}}">Next »</a>
{% endpaginate %}Paginate object
Inside the paginate block, a paginate object is available with the following attributes.
current_page: the current page, a number.items: an array of items in the slice of the inputobject_arraycorresponding to the current page.page_count: the number of pages.pages: an array of objects representing the pagination pages. All objects inpageshave the attributesurl(returning the url of a pagination page, e.g. /this-url?page=3),index(the pagination page’s index number),is_link(whether the pagination page is a link or not).is_linkreturns false at the current pagination page or if the page falls outside thewindow_size(in which case it’s merely a ‘…’).next: represents the next pagination page. Also hasurl,indexandis_linkattributes.previous: represents the previous pagination page. Also hasurl,indexandis_linkattributes.
Example Pagination
This is a typical pagination example. The important part is using the pagination_page.is_link and check the weird ellipsis html entity.
This allows for proper active and disabled styling.
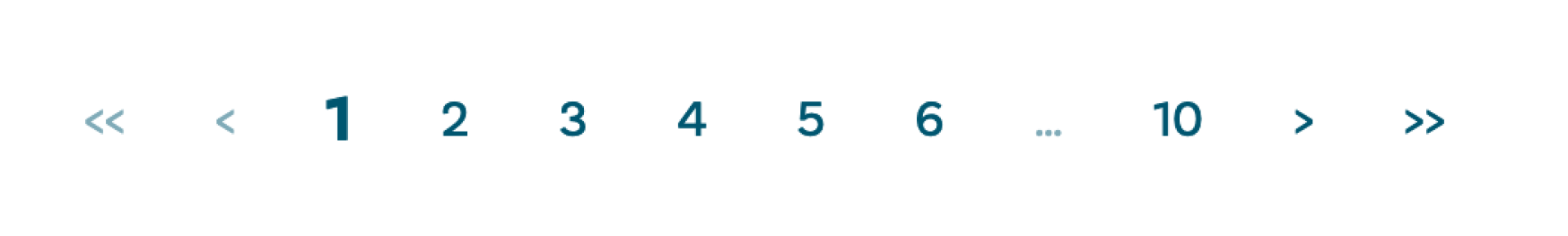
<div class="pagination">
<div class="pagination-list">
{%- if paginate.pages[0] -%}
<ul class="pagination-list">
<li class="pagination__item pagination__item--start">
<a {% if paginate.previous == blank %}class="disabled"{% else %}href="{{ paginate.pages.first.url }}"{% endif %}>
<span><<</span>
</a>
</li>
<li class="pagination__item pagination__item--prev">
<a {% if paginate.previous != blank %}href="{{paginate.previous.url}}"{% else %}class="disabled"{% endif %} title="{{"views.previous" | translate }}">
<span><</span>
</a>
</li>
{% for pagination_page in paginate.pages %}
<li class="pagination__item {% if pagination_page.is_link == false and pagination_page.index != "…" %}pagination__item--active{% endif %}">
<a {% if pagination_page.index contains "…" %}class="disabled" {% else %}href="{{ pagination_page.url }}"{% endif %}>
<span>{{ pagination_page.index }}</span>
</a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
<li class="pagination__item pagination__item--next">
<a {% if paginate.next != blank %}href="{{paginate.next.url}}"{% else %}class="disabled"{% endif %} title="{{"views.next" | translate }}">
<span>></span>
</a>
</li>
<li class="pagination__item pagination__item--end">
<a {% if paginate.next == blank %}class="disabled"{% else %}href="{{ paginate.pages.last.url }}"{% endif %}>
<span>>></span>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
{%- endif -%}
</div>
</div>